PTO Shaft short for Power Take-Off shaft, is a mechanical component that transfers power from an engine (usually in a vehicle like a PTO tractor or PTO truck) to auxiliary equipment. This could be anything from a hay baler to a dump truck’s hydraulic system.
Instead of requiring a separate engine for each piece of powered equipment, a PTO allows the main engine to do the heavy lifting — both figuratively and literally. It’s energy efficiency in action.
Think of it like an electrical outlet… for machines. You just “plug in” a tool and boom — that spinning output powers your entire implement or system.
How Does a Power Take-Off Shaft Actually Work?
The power take-off shaft connects to the vehicle’s engine output using a yoke and transfers rotary force to another machine. Typically, it involves three main stages:
- Power Generation – Engine produces torque.
- Transmission – PTO transfers that torque through the shaft.
- Output Activation – The implement (e.g., mower, spray pump) starts working.
In modern machinery, PTO shafts include telescoping shafts, slip clutches, and shielding for safety and durability. Standard designs today are more versatile, thanks to better materials and flexible couplings.
Real-World Example: PTO on a Mid-Size Tractor
“I upgraded to a newer PTO tractor for hay baling, and it cut my round baling time down by half. More torque, same fuel. PTO makes all the difference.”
In this case, a hobby farmer based in Arizona used a PTO shaft to power a new baler. By switching from an older belt-based transmission to a shaft-driven PTO system, the result was faster, smoother baling — no overheating, no mid-field breakdowns.
Such applications reveal the understated but game-changing nature of PTO systems in the field.
PTO Shafts in Heavy-Duty Trucks — How It Works for PTO Trucks
While tractors dominate the conversation, the PTO truck is just as relevant.
In dump trucks, cement mixers, and fire engines, a PTO shaft is mounted directly to the transmission (not the engine per se). This setup activates machinery like a boom crane or hydraulic hoist — essentially turning the truck into a mobile workhorse.
Common PTO Truck Uses:
- Hydraulic lifts (dump trucks, tow trucks)
- Utility line repair equipment
- Mobile concrete mixers
- Severe-duty fire engines
Today, smart PTO systems integrate tech like torque sensors and on-demand synchronization, helping trucks avoid wasting fuel when idle — a big step for emissions control in 2025.
Benefits of Using PTO Shafts in 2025
PTO technology has matured far beyond its WWII-era roots. Here’s what makes them indispensable today:
Efficiency:
No need for multiple engines — one engine powers multiple systems. Saves fuel, time, and wear.
Reliability:
Solid mechanical design with fewer complicated electronics (compared to hydraulic-only setups).
Flexibility:
Supports a massive range of tools — from agricultural equipment to commercial hydraulic systems.
Safety (When Used Right):
Today’s PTO shafts often include guards, slip clutches, and advanced kill switches.
But, be warned…
Risks & Safety Considerations
PTO shafts, while efficient, are not without danger. One wrong move and the rotating force can cause serious injury or worse.
Here’s what you MUST consider before operating:
- Never step over a running PTO.
- Always check protective guards.
- Disconnect power completely before maintenance.
According to mechanical safety audits in late 2024, over 60% of PTO-related injuries happened due to missing shielding and loose clothing. Automation can help — but user awareness is everything.
Types of PTO Shafts (2025 Update)
In 2025, we now have more configurations based on performance, size, and application.
By Connection Type:
- 1-3/8” 6-spline: Most common for mid-size tractors
- 1-3/4” 20-spline: Found in high-HP machinery
- Flanged PTO†: Seen in large commercial/industrial use
By Speed/Rotation:
- 540 RPM: Smaller tools; lighter tasks
- 1000 RPM: For bigger, power-hungry equipment
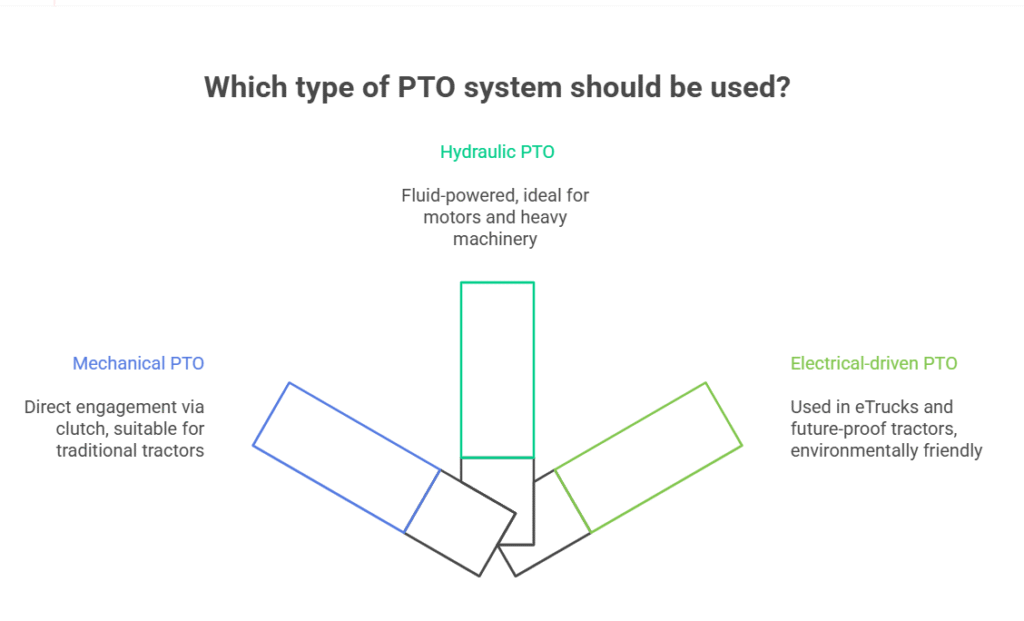
By Technology:
- Mechanical PTO: Direct engagement via clutch
- Hydraulic PTO: Fluid-powered, typically used with motors
- Electrical-driven PTO hybrids: Used in eTrucks and future-proof tractors
Different PTO tractor models and PTO truck setups will come fitted with compatible shafts — always check your user manual or contact the manufacturer.
Maintenance Tips: Keep Your PTO Running Strong
Proper care means better output and longer lifespan. Here’s how to avoid downtime:
- Grease every 8–10 hours of use
- Inspect yokes and cross bearings monthly
- Ensure shielding is snug and undamaged
- Store PTO shaft indoors, clean and dry
A neglected shaft can become unbalanced, which risks joint failure, vibration damage, and even transmission breakage.
How PTO Shafts Fit Into Sustainability Goals
With modern PTO tractor models trending toward hybrid and fully electric, engineers are revisiting the efficiency benefits of PTO power systems. Less fuel usage — and more intelligent power sharing.
Some PTO systems are now connected to AI load balancers that distribute power based on terrain stability and engine load. This saves energy and extends the life of both vehicle and implement.
Plus, remote monitoring from mobile apps allows for real-time diagnostics, alerts, and performance stats — perfect for farmers managing multiple units over hundreds of acres.
Comparing PTO Shaft Power vs Other Drive Systems
| Drive System | Power Transfer | Maintenance | Efficiency | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTO Shaft | Direct shaft | Moderate | High | Farming, Trucks, Industrial |
| Hydraulic Motor | Fluid | High | Medium | Precision tools, factory settings |
| Belt Drive | Friction | High | Low | Small tools, hobby use |
| Electric Motor | Wire-fed | Low | Varies | Modern tractors, labs |
Choosing between a PTO shaft and alternatives comes down to workload, budget, and environment.
Fun Fact
The original patent for a mechanical PTO was filed in the 1920s — and guess what? The concept hasn’t changed much. Why mess with something that just works?
FAQs
Q. What does a PTO shaft do on a tractor?
A. PTO shaft transfers mechanical power from the tractor’s engine to an attached implement (like a mower, baler, or sprayer). It essentially allows the tractor to “drive” other equipment without requiring independent engines.
Q. How do I know what PTO shaft I need?
A. Check your equipment’s required RPM (usually 540 or 1000) and shaft size (e.g., 6-spline). Manufacturers list this in the owner’s manual or on the equipment nameplate.
Q. Can a PTO shaft work on any tractor?
A. Not exactly. You need to ensure the PTO output (size, spline count, and RPM) on your tractor matches the implement. Some tractors have interchangeable or dual-speed PTO options to broaden compatibility.
Q. Are PTO shafts safe to use?
A. Yes — but only when used correctly. Always use shaft guards, avoid loose clothing, and never approach a spinning shaft. Newer shafts also come with kill-switch options and added shielding for extra safety.
Final Thoughts
In this era of agri-tech, electric vehicles, and smart gear — the humble PTO shaft still holds its ground as a rock-solid, effective power delivery method. It’s efficient, adaptable, and essential in everything from a PTO truck hauling debris to a PTO tractor rows deep into a harvest field.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
There’s a certain weight in the words John Authers writes—not just because of what he knows, but how he shares it. His voice doesn’t just echo facts; it builds meaning. In a world overwhelmed by rushed opinions and robotic summaries, John’s writing feels… different. It feels lived-in, thoughtful, and deeply human.
Readers don’t turn to John for headlines—they come for context. They come for that rare blend of clarity, insight, and emotional depth that turns financial journalism into something closer to storytelling. His reflections on markets, geopolitics, or human behavior aren’t just readable—they’re relatable.
What sets John apart isn’t just his experience (though he has plenty of it). It’s his ability to pause, reflect, and explain the why behind the what. He writes like someone who’s been in the room where it happens—but never forgets the reader who hasn’t.
In 2025, when AI churns out articles in milliseconds, John Authers still writes like a human—and that, more than anything, is what makes his work worth reading.