Feedback loop is a circular system where the output of a process loops back as input to influence the next cycle. Think of it like a conversation:
You say something (input).
The other person responds (output).
You hear their response (feedback) and adjust what you say next (new input).
Feedback loops fall into two categories:
- Negative Feedback Loops: They reduce change to maintain balance (like your thermostat keeping the room at 72°F).
- Positive Feedback Loops: They amplify change to achieve a goal (like blood clotting to stop bleeding).
Sounds abstract? Let’s ground it in real life.
Feedback Loop Diagram: Visualizing the Magic
Here’s a simple feedback loop diagram for a home heating system:
text[Temperature Sensor] → [Thermostat] → [Heater]
↑ ↓
[Current Room Temp] ← [Heat Output]
- The sensor checks the room temperature (input).
- If it’s below 72°F, the thermostat tells the heater to warm up (output).
- The heater raises the temperature (feedback).
- The sensor detects the change and adjusts the heater (loop repeats).
This negative feedback loop ensures your living room never freezes or turns into a sauna.
Blood Clotting: A Life-Saving Positive Feedback Loop
When you cut yourself, your body doesn’t just shrug and say, “Oh, a little blood never hurt anyone.” Nope, it unleashes a blood clotting positive feedback loop faster than you can say “Band-Aid.”
Here’s how it works:
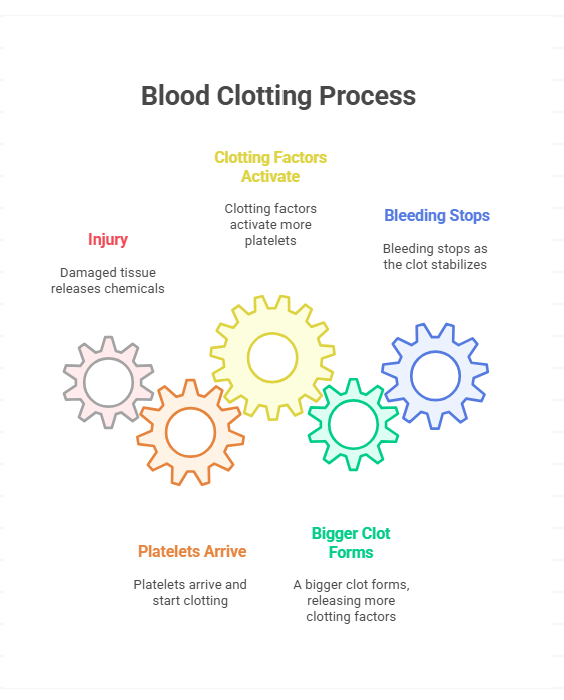
- Injury → Damaged tissue releases chemicals (input).
- Platelets arrive and start clotting (output).
- Clotting factors activate more platelets (feedback).
- Bigger clot forms, releasing even more clotting factors (amplified output).
- Bleeding stops (goal achieved).
This positive feedback loop turbocharges the process. Without it, you’d bleed out from a paper cut.
Real-Life Example: A hemophiliac’s body struggles to create this feedback loop. Even minor injuries become life-threatening because their clotting factors don’t amplify properly. Modern treatments mimic this loop artificially to save lives.
Homeostasis and Feedback Loops: The Body’s Balancing Act
Your body is a master of homeostasis—keeping internal conditions stable despite external chaos. Feedback loops are its secret weapon.
Examples:
- Temperature Regulation: Sweat (cooling) or shiver (heating) loops keep you at 98.6°F.
- Blood Sugar Control: Insulin (lowers sugar) and glucagon (raises sugar) loops prevent diabetes.
- Breathing: CO₂ levels trigger feedback loops to speed up or slow down breathing.
Negative feedback loops dominate here because balance is the goal. No one wants their heart rate spiking like a positive feedback loop during a marathon (unless you’re sprinting for the finish line).
Loops Feedback in Technology: AI, Algorithms, and Beyond
Now, let’s shift gears to the digital world. Feedback loops power everything from Google’s search rankings to your Instagram feed.
How Social Media Uses Feedback Loops:
- You like a post (input).
- The algorithm shows you similar content (output).
- You engage more (feedback).
- The algorithm adapts, showing even more tailored posts (loop repeats).
This positive feedback loop keeps you scrolling endlessly (sorry, not sorry).
AI and Machine Learning: Neural networks learn via feedback loops:
- AI predicts a cat in an image (output).
- You correct it (feedback: “No, it’s a dog”).
- AI adjusts its model (new input).
- Next time, it gets “dog” right (goal achieved).
Real-Life Quote: “Our AI model improved by 40% in one month just by tweaking the feedback loop mechanism. It’s like teaching a child—the more corrections, the smarter they get.”
The Dark Side of Feedback Loops: When They Go Rogue
Not all loops feedback systems are beneficial. Runaway feedback loops cause:
- Audio Feedback: That ear-piercing squeal from the stage mic.
- Market Crashes: Automated trading algorithms amplifying sell-offs.
- Ecosystem Collapse: Overpopulation in a species triggering irreversible damage.
The Fix: Introduce dampening mechanisms (like volume controls or circuit breakers) to stop the loop from spiraling out of control.
Creating Your Own Feedback Loop Diagram
Want to visualize any system? Follow these steps:
- Identify the Goal: What are you trying to achieve (e.g., stable temperature)?
- Map Inputs and Outputs: Sensors, actuators, and decision points.
- Draw the Loop: Connect output back to input.
- Label Feedback: Positive (amplifies) or negative (reduces).
For example, here’s a feedback loop diagram for learning a new language:
text[Language App] → [Lessons] → [User Progress]
↑ ↓
[Quiz Results] ← [Practice Output]
The app adjusts lessons based on your quiz scores (feedback). Loop repeats until you’re fluent.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What’s the difference between positive and negative feedback loops?
A: Negative loops reduce change (maintain balance), while positive loops amplify it (achieve a goal fast). Think thermostat vs. blood clotting.
Q2: How do feedback loops apply to business processes?
A: Companies use them for continuous improvement. Customer feedback (input) improves products (output), which generates more feedback (loop). Example: Netflix refining recommendations.
Q3: Can feedback loops be harmful in technology?
A: Absolutely. Runaway loops cause server crashes, infinite bugs, or AI hallucinations (e.g., chatbot spamming nonsense). Add rate limiting to control them.
Q4: Are feedback loops only digital?
A: No! Biology (your body), ecology (predator-prey cycles), and even economies (supply-demand) rely on loops feedback. Nature invented this mechanism billions of years ago
The Future of Loops Feedback: Smarter, Faster, Better
- AI Self-Improvement: Neural networks optimizing their feedback loops autonomously.
- Smart Cities: Traffic lights adjusting in real-time via IoT feedback loops.
- Personalized Medicine: Treatment plans adapting to patient feedback (symptoms, genetics).
- Quantum Computing: Error correction loops pushing computing limits.
Feedback loops aren’t just a tech buzzword; they’re the DNA of progress—natural, digital, and everywhere in between.
Conclusion
Loops feedback in action—from your immune system to Instagram’s algorithm—it’s time to apply this magic in your world:
- Optimize your workflows with continuous feedback.
- Design smarter systems using feedback loop diagrams.
- Explore AI tools that learn from loops feedback.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
There’s a certain weight in the words John Authers writes—not just because of what he knows, but how he shares it. His voice doesn’t just echo facts; it builds meaning. In a world overwhelmed by rushed opinions and robotic summaries, John’s writing feels… different. It feels lived-in, thoughtful, and deeply human.
Readers don’t turn to John for headlines—they come for context. They come for that rare blend of clarity, insight, and emotional depth that turns financial journalism into something closer to storytelling. His reflections on markets, geopolitics, or human behavior aren’t just readable—they’re relatable.
What sets John apart isn’t just his experience (though he has plenty of it). It’s his ability to pause, reflect, and explain the why behind the what. He writes like someone who’s been in the room where it happens—but never forgets the reader who hasn’t.
In 2025, when AI churns out articles in milliseconds, John Authers still writes like a human—and that, more than anything, is what makes his work worth reading.